Earth Observation for Rapid Burned Area Mapping (R-BAM)
Client
Canadian Space Agency (CSA)
Location
Canada (various locations)
Project Duration
November 2016 – November 2018
Background
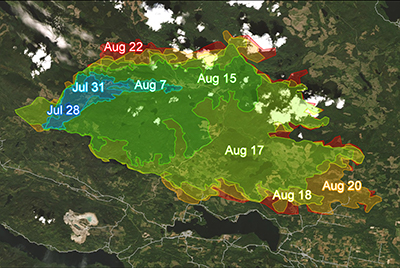
With wildfire frequency and intensity increasing across many parts of the world, government agencies, private companies, and First Nations require timely and accurate information to assess wildfire burn areas and progression. The Rapid Burned Area Mapping (R-BAM) technology was required to complement conventional wildfire observation and assessment techniques in support of wildfire response and recovery efforts.
Services Provided
Hatfield developed R-BAM tools to provide new methods to combine optical/thermal and radar satellite Earth observation (EO) data with machine learning analytics.
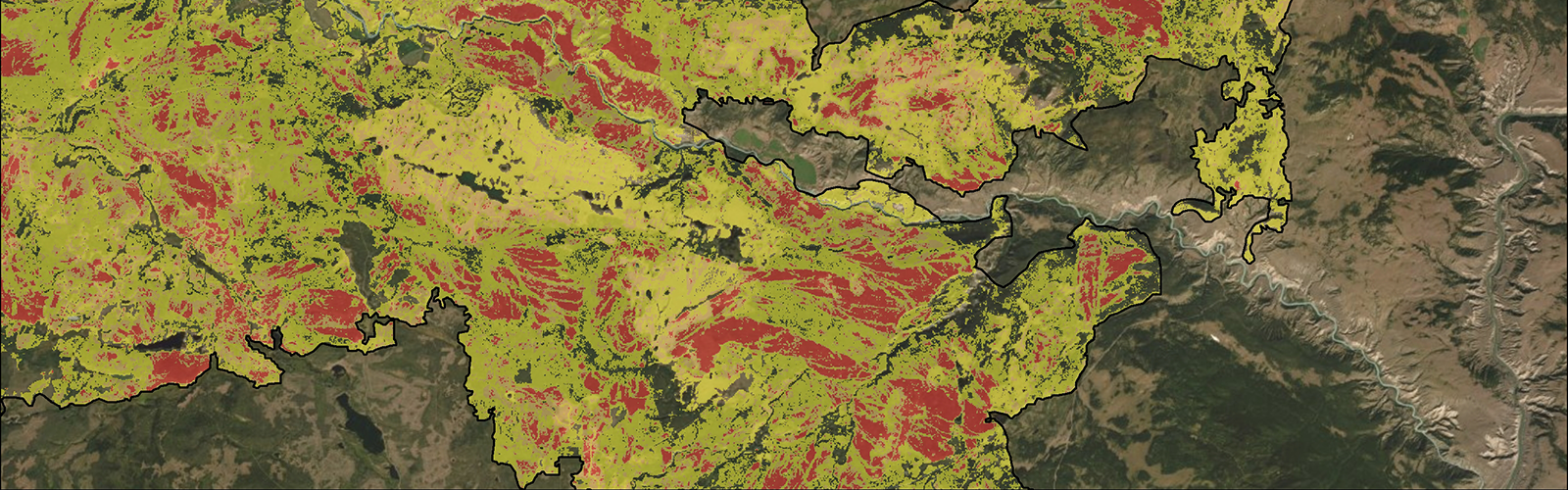
R-BAM Optical Services and Tools provide automated workflows that process multispectral EO time series data in order to create cloud-free composite images to assess burn severity through change detection analysis as a wildfire progresses. The advanced R-BAM algorithms incorporate Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 imagery to create maps and geospatial data that support wildfire response and recovery.
R-BAM Radar Services and Tools were developed because radar data have the capability to operate in the presence of clouds, haze, and smoke. Radar is sensitive to the change in the structural characteristics of a forest when a wildfire occurs, which can be used to map burned areas. Hatfield assessed the potential for radar data to contribute to wildfire progression monitoring, including factors that may affect the reliability of information extraction from radar, such as forest type, topography, and moisture conditions.